By retaining a portion of its profits as undistributed profit, a company can build up its equity reserves and reduce its reliance on external sources of funding. When a recession hits and consumer spending decreases, the company faces a drop in revenue. However, it can rely on its undistributed profit to cover operating costs, retain skilled employees, and keep the business afloat until economic conditions improve. Retained earnings, on the other hand, specifically refer to the portion of a company’s profits that remain within the business instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends. If a company decides not to pay dividends, and instead keeps all of its profits for internal use, then the retained earnings balance increases by the full amount of net income, also called net profit. Retained earnings are also known as accumulated earnings, earned surplus, undistributed profits, or retained income.
Retained earnings could be used for funding an expansion or paying dividends to shareholders at a later date. Retained earnings are related to net (as opposed to gross) income because they are the net income amount saved by a company over time. Undivided profits refer to gains from current and past years that have not been transferred to a surplus account or distributed as dividends to shareholders. Often times, financial gains or budget surpluses are set aside in a separate account designated as a surplus account, are earmarked for distribution as dividends, or assigned to another purpose such as funding a project.
Understanding Undivided Profit
Instead of seeking external funding, the company uses its retained earnings to finance research and development, production, and marketing. This strategic use of undistributed profit enables the company to grow without taking on additional debt or diluting ownership by issuing more shares. It reconciles the beginning balance of net income or loss undistributed profits that have accumulated in the company over time are called for the period, subtracts dividends paid to shareholders and provides the ending balance of retained earnings. Based on this, the firm contended that bookkeeping, VAT, payroll and preparatory work undertaken by junior staff to prepare financial statements and audit files for review by qualified accountants were non-professional services.
- The goal of underlying profit is to eliminate the impact that random events, such as a natural disaster, have on earnings.
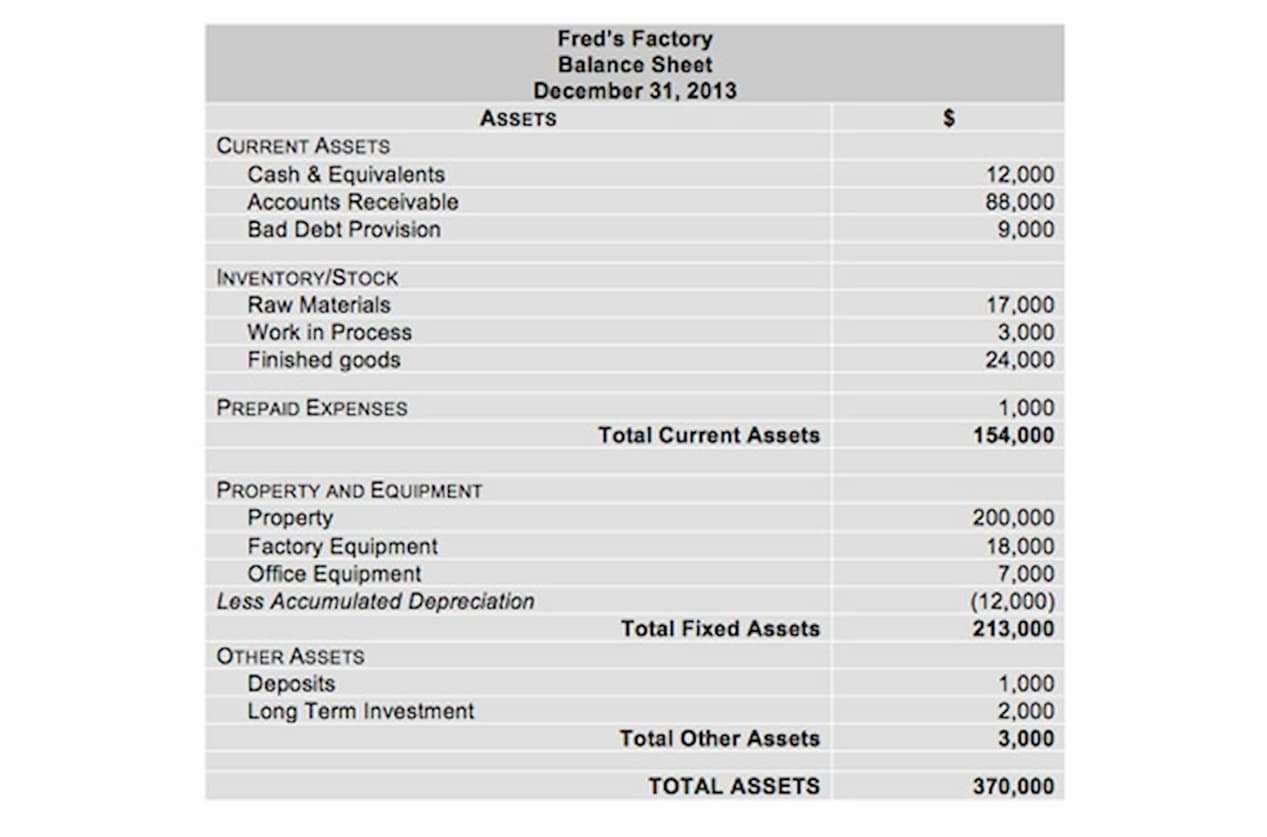
- Retained earnings are reported in the shareholders’ equity section of a balance sheet.
- Retained earnings refer to the money your company keeps for itself after paying out dividends to shareholders.
- Net profit (also called net income or net earnings) is the value that remains after all expenses, including interest and taxes, have been deducted from revenue.
- However, the revenue and expenditure transactions related to the Capital Account on the receipt of profits and the recognition of capital contribution by investors are not specified.
The accumulated earnings of a firm are profits generated, but not distributed to the shareholders as cash dividends or as corporate profit taxes. Instead, they are retained to be reinvested in a new business opportunity, to increase inventory levels, to lower long-term debt or to increase cash reserves. Undistributed profit is a financial concept that plays a crucial role in a company’s financial health and planning. It refers to the portion of a company’s earnings that is retained within the business rather than being distributed to shareholders as dividends. In this guide, we’ll break down the concept of undistributed profit in simple terms, explore its significance for companies, and provide examples to illustrate its impact on financial decision-making. Retained earnings can typically be found on a company’s balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section.
Accounting Profit vs. Underlying Profit
Therefore, a company with a large retained earnings balance may be well-positioned to purchase new assets in the future or offer increased dividend payments to its shareholders. Current earnings may be credited to the undivided profits account and will eventually either be distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends or will be held within the company in the form of retained earnings. Dividend distributions signal strong financial strength within the company while retained earnings can be used to further future growth. The desired strategy may depend on the amount of profit generated and the potential for value-maximizing projects.
Alternatively, the company paying large dividends that exceed the other figures can also lead to the retained earnings going negative. Cash payment of dividends leads to cash outflow and is recorded in the books and accounts as net reductions. As the company loses ownership of its liquid assets in the form of cash dividends, it reduces the company’s asset value on the balance sheet, thereby impacting RE. Retained earnings refer to the historical profits earned by a company, minus any dividends it paid in the past.
To surcharge or not?
Cash flow and profit are both important metrics when evaluating a company’s performance, and each has its pros and cons as a metric. Unsurprisingly, the Commissioner also regarded the significant one-off assignment in 2012 (a company valuation) as a professional service. Similarly, the iPhone maker, whose fiscal year ends in September, had $70.4 billion in retained earnings as of September 2018. Retained earnings and profits are related concepts, but they’re not exactly the same. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Profit is a widely monitored financial metric that is regularly used to evaluate the health of a company.
However, the revenue and expenditure transactions related to the Capital Account on the receipt of profits and the recognition of capital contribution by investors are not specified. Banks before carrying out capital increase procedures at the Department of Planning and Investment. The surcharge applies where the principal part of a close company’s income is derived from surchargeable activities (in this case the provision of professional services). Where they differ is that economic profit also uses implicit costs; the various opportunity costs a company incurs when allocating resources elsewhere. The retained earnings are calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting net losses from) the previous term’s retained earnings and then subtracting any net dividend(s) paid to the shareholders. In the long run, such initiatives may lead to better returns for the company shareholders instead of those gained from dividend payouts.
Last modified: September 13, 2024
